Please Use Internet Explorer 5 or Over.
Ó Copyright 2004 by
Author’s
E-mail address: yaoyanyy2000@yahoo.com.au
6.
Quantum Mechanics, QED and Other Related Theories
Contents
![]() 6.1. Entity Field Theory and
Quantum Mechanics
6.1. Entity Field Theory and
Quantum Mechanics
![]() 6.2.
Entity Field Theory and QED
6.2.
Entity Field Theory and QED
Note:
Since the purpose of entity field physics is to correct the mistakes in classical physics with concepts of modern physics, it can be understood as a modernized classical physics. It provides direct links to all concepts in modern physics.
6.1. Entity Field Theory and Quantum Mechanics
A moving electron is a particle carries electromagnetic wave for it has a particle, an entity electric field and an entity magnetic field in its structure. It will move along a straight track by itself unless affected by other electric or magnetic force. This is one of the foundations of quantum-mechanics and QED.
An electron in a beam of electrons acts like wave due to the interaction between electrons. The diffraction of electron beam is caused by the electric and magnetic forces of a material interacting with every passing electron. Once a moving electron is stopped, it will release its entity magnetic field as a photon carrying electromagnetic wave, so a stationary electron does not carry electromagnetic wave.
Other moving particles also carry electromagnetic wave (including neutron and atom) due to the entity electric and magnetic fields in their structures. The wave length of a moving particle is
![]() (6.1.1)
(6.1.1)
It says that if the speed of the particle becomes zero, there is no wave any more.
The energy of a moving particle is
![]() (6.1.2)
(6.1.2)
Entity field theory provides direct links to other important results of quantum-mechanics.
Wave function: Since a moving particle carries electromagnetic wave, it can be described by the wave function y(x, t) as defined in quantum mechanics. This is the other foundation of quantum-mechanics
Spin of a moving electron: A moving electron has an entity magnetic field in its structure. This entity magnetic field has innate N pole and S pole of its magnetic force. These two poles are calculated as spins of a moving electron. There is no spin for a stationary electron since there is no entity magnetic field in it.
Uncertainty principle: Since an stationary electron is protected by an electric force field and a moving electron is protected by an electric force field and a magnetic force field, there is no way to approach an electron without affecting its original state.
6.2. Entity Field Theory and QED
Entity field theory also provides direct links with QED. In both theories, a particle is treated as a particle in free space and as a wave during an interaction.
For any moving particle, its track is along a straight line unless an interaction occurred. If we can accurately calculate all the interactions, we can trace out its motion step by step. The more steps it involves, the more accurate the final result will be. Theoretically, this method can be used for any physical process. This is why QED is called physics for everything.
Since entity field theory is to modernize classical physics with the concepts of modern physics, some basic concepts of QED are built in the theory and do not have to be explained again here. For example: the concept of a virtual photon in QED is the original model of entity electric and magnetic fields in the structure of a moving electron, they are the same thing with different manes. Other common concepts are: photon, interaction, scattering of a particle, etc.
In entity field theory, both entity electric and magnetic fields are quantified fields, their force fields can also be quantified as treated in QED and other related modern physics theories.
6.3. Elementary Particles
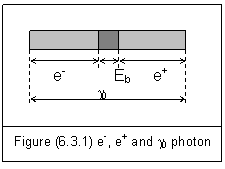
In QED, pair production and pair annihilation must have more than one photon involved. This rule is no longer valid in entity field theory. The structure of a photon decided that one photon can be split into a pair of electron and positron in pair production; and one photon can be produced in pair annihilation.
In entity field theory, a photon is the basic unit of an independent entity field. It can be an electric photon or a magnetic photon as the result of its property wave.
An electric photon can be understood as a pair of electric particles bound together by electric energy. It can be split into two electric particles if an interaction can overcome the binding energy. A typical example of this kind of split is pair production
g0®e-+e+ (6.3.1)
Where g0 is a g-ray photon; e- is an electron and e+ is a positron.
Mass-energy conservation of pair production is
hn+Eb=2m0c2 (6.3.2)
Where Eb is binding energy within the g0 photon; m0 is rest mass of an electron or a positron.
The opposite process of pair production is pair annihilation
e-+e+®g0 (6.3.3)
It has the same mass-energy conservation as pair production.
Since the structure of a g0 photon has an electron and a positron, both pair production and pair annihilation can be described in figure (5.3.1).
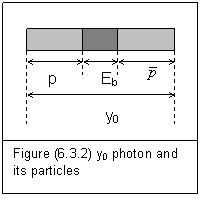
Similarly, a pair of proton-antiproton can also be created by pair production of a photon with certain energy. Because the energy of this field quantum is unknown yet, we could call it as y0 photon
![]() (6.3.4)
(6.3.4)
Its mass-energy conservation is
hn+Eb=2mpc2 (6.3.5)
There is also pair annihilation of proton and antiproton
![]() (6.3.6)
(6.3.6)
Both the above pair production and pair annihilation can be described in figure (5.3.2).
There is also experiment of pair production of neutron-antineutron. In entity field theory, a neutron can also come from the combination of electron and proton as we discussed before. This is to say that electron and proton are all we need to build up nucleus, atom, molecule and the whole world.
Due to the fact that pair production producing particles and antiparticles, antiparticles can also build up an anti-world somewhere in the universe.
If an object, which is made of elementary particles, hit another object, which is made of antiparticles, the two objects will get into a process of annihilation. Particles and antiparticles from both objects will be annihilated into electromagnetic wave. Depending on the masses, speeds and hitting tracks of the two objects, they can form different kind of stars. This is to say that any star, including the sun, is formed as the result of annihilation.
The electromagnetic wave from this annihilation is the end of involved particles and antiparticles, but it is also the beginning of new particles and antiparticles. Due to the pair production, a new world and anti-world can be rebuilt again by nature.
Entity field physics will have great impact on science and technology.